Features of New Generation SIEMs
Features of New Generation SIEMs
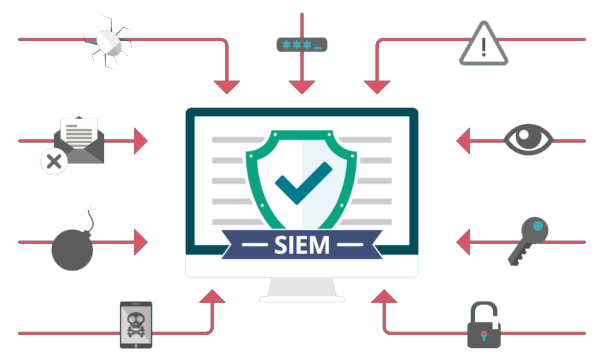
Early detection, rapid response and collaboration are imperatives to overcome today's advanced threats. But these requirements are heavy demands on a security team. Today, monitoring and reporting on security logs and events is no longer enough, and security professionals need a broader view of all data sources in all parts of the organization. To stay ahead of external attacks and internal attackers, the company needs an advanced security solution that can quickly respond, investigate and investigate incidents and handle breach scenarios. Computer incident relief management and coordination center be used In addition, the company needs the ability to detect and respond to known and unknown advanced threats. In the center of security systems, a solution Strong security information and events That in short SIEM It is called, there is. This platform fully monitors the environment and provides a wide view of it. In the continuation of this article, we will examine the new key criteria and capabilities that New generation SIEMs They need to provide them, it will be paid.
New benchmarks for next-generation SIEMs
The organization's security team must have one SIEM tools use that, in addition to solving common use cases, also provide solutions for solving advanced security use cases. It is expected to keep up with the dynamic threat landscape Modern SIEMs Able to:
- Centralization and integration of all security-related events at the same time as they occur.
- support various collection mechanisms such as syslog, file transmissions, file collections, etc.
- Add threat intelligence and environmental intelligence to security events.
- Perform correlation and alerting on a wide range of data.
- Detection of advanced and unknown threats.
- Create behavioral profiles throughout the organization.
- Collect all data and make it available for uses such as monitoring, alerting, research and investigation, and ad hoc search.
- Providing the possibility of ad hoc search and reporting on data in line with advanced breach analysis.
- Investigate incidents and lead forensic investigations to investigate incidents in detail.
- Check the status of compliance with the requirements and report on this.
- Practical use of analyzes and reports on the security situation.
- Track attacker activities with ad hoc analysis and event sequencing.
- to assess threats from apps and cloud data sources, on-premise and hybrid.
Today, all data is related to security.
Evidence of an attack, as well as its activities, exists in an organization's data. In order for security teams to properly investigate security incidents and identify threats, they need all data, not just security data obtained from traditional security products such as Firewalls, IDS or anti malware, To SIEM be given Organizations lose most of the data needed to see their security status in time. The activities of these advanced threats often exist only in non-security related data such as operating system logs, directory systems such as LDAP/AD, DNS, and web and email servers. Machine data often needs to be associated with internal and external environmental threats to aid in incident response and breach detection.
Keeping pace with the volume and scale of data
The amount and type of data required to make the most effective data-driven security decisions requires a solution capable of indexing hundreds of terabytes of data per day without normalization at the time of schema collection and application.[1] to this data at the time of search.
Automatic detection of anomalies and disorders
For advanced threat detection, all security-related and non-security-related data must be stored in a single repository. The volume of this reservoir is large and can be used as a basis for defining user and normal traffic behaviors. Using this starting point, analytics can detect anomalies and disruptions that may pose an advanced threat. Statistical methods can help with this diagnosis by looking for events that deviate from the normal pattern. Correlation can also help detect rare and suspicious combinations of events.
A new approach to SIEM
SIEMThere are many that claim to provide the necessary new standards, but this may not be the case SIEMها Not suitable for your organization. The following table shows key capabilities for evaluation New generation SIEM Or re-evaluate a traditional SIEM display:
Key feature | value that can be created |
Being a single platform | The need to install and manage only one product, which will lead to the simplification of operations |
software | By using common hardware, hardware costs will be minimized |
Indexing of all data using various techniques | Rapid Productivity: Value Customers SIEM They understand themselves in a few hours or days |
A large number of predefined data sources | Dependency on the seller SIEM And dedicated input data sources are reduced |
A flat data warehouse that provides access to all data values and data filters without any schema or normalization. | All values and fields from all data sources are searchable and reportable and can be correlated as predefined alerts or for ad hoc research. |
Single data warehouse with indexing and distributed search | There are no other problems related to scalability and speed |
Flexible search for automated initial profiling and advanced correlation | Increasing the ability to detect disorders and abnormalities |
Visualize data and events in multiple formats | The ability to use, create and edit tables, charts or scatter plots provides a large part of the flexibility needed to suit a variety of customer environments. |
Unlimited support for APIs and SDKs | To expand capabilities SIEM Connects with third-party apps |
Support common IT use cases such as compliance enforcement, fraud, theft and abuse detection, IT operations, service intelligence, etc. | As security teams work in concert with other IT functions, visibility gained from other use cases leads to centralized visibility across the organization. |
Use in cloud, on-premise and hybrid environments | Use a logical solution that allows users to search, report, and work with data regardless of where the data is stored. |
Option to expand to cloud (BYOL و SaaS) | It helps to consolidate the business in the cloud |
Hybrid deployment with on-premises and cloud options | Optimizing business needs with SaaS and on-premise applications without sacrificing security visibility |
Response actions | It improves operational efficiency with automated and human-assisted decisions |
Actionable threat intelligence | Security teams can quickly and efficiently turn threat intelligence into actionable intelligence to identify threats and protect the organization. |
Scoring the risks | The relative risk of a device or user in the network of your environment is known over time |
Ad hoc search on extended time periods | To achieve a deep and accurate insight, it identifies breaches by delving into machine data and analyzes them accurately. |
Support for the Kill chain research method | Gain visibility into an attack, understand adversary targets, monitor activity during an attack, store key information and use it to defend your organization |
Support for five defense styles against advanced threats | Help detect advanced targeted attacks in near real-time and post-intrusion |
Platform flexibility and architecture play a key role in scalability considerations SIEM To achieve the needs of the organization. This is an important issue that software SIEM It is scalable and can quickly index all original raw data in a very large volume (from several terabytes to several petabytes per day).
Horizontal scalability using common hardware provides computational flexibility and scalability that expensive physical appliances cannot provide.
The use of distributed indexing and search technologies with fast search, reporting and analytics enables rapid transfer of results to a wide range of reports and interactive visualizations.